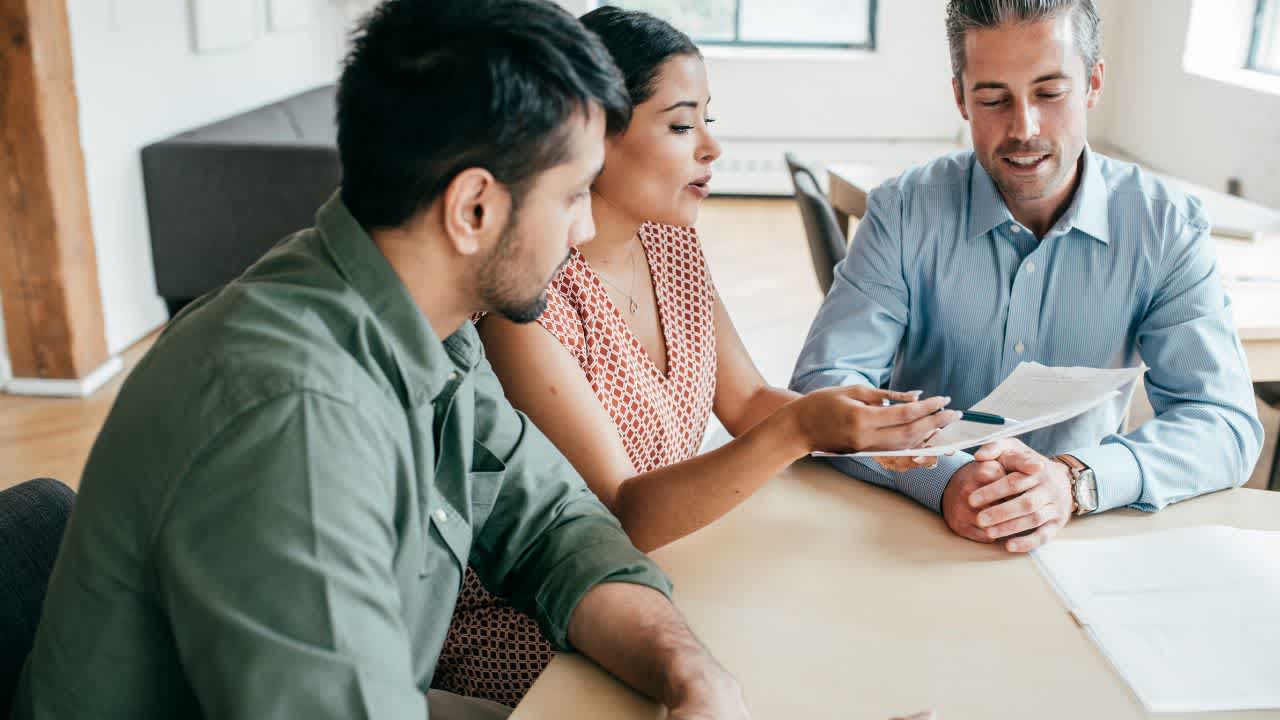
Mental health surveys questions and issues can have a significant impact on an individual’s ability to perform effectively in the workplace. Here are some ways in which mental health issues can affect work:
Decreased Productivity: Mental health challenges such as anxiety, depression, or stress can lead to decreased focus, concentration, and overall productivity. Completing tasks may take longer, and the quality of work may suffer.
Absenteeism: Individuals with mental health issues are more likely to take frequent sick days or time off due to their symptoms. This can disrupt workflow, strain team dynamics, and increase the workload on other employees.
Presenteeism: Even when physically present at work, individuals experiencing mental health difficulties may struggle to engage fully in their tasks. This “presenteeism” can lead to reduced efficiency and subpar work quality.
Interpersonal Challenges: Mental health issues can affect communication and collaboration with colleagues. Individuals might withdraw socially, have difficulty engaging in team activities, or experience conflicts with coworkers due to their symptoms.
Decision-Making: Poor mental health can impair a person’s ability to make sound decisions. This could lead to errors in judgment, inappropriate risk-taking, or difficulty in assessing situations accurately.
Workplace Relationships: Mental health challenges can strain relationships with supervisors, peers, and subordinates. Mood swings, irritability, or withdrawal might lead to misunderstandings and conflicts.
Creativity and Innovation: Mental health struggles can hinder creative thinking and innovation. Individuals may find it difficult to generate new ideas or approach problems from different angles.
Job Satisfaction: Employees facing mental health difficulties may experience decreased job satisfaction due to their struggles with work-related stressors, role demands, and overall well-being.
Career Advancement: Untreated mental health issues might limit an individual’s ability to take on new responsibilities, participate in career development opportunities, or compete for promotions.
Physical Health Impact: Mental health problems can lead to physical symptoms like fatigue, sleep disturbances, and somatic complaints. These physical symptoms can further exacerbate work-related challenges.
Burnout: Prolonged exposure to high levels of stress and mental health challenges can contribute to burnout, characterized by emotional exhaustion, cynicism, and reduced professional efficacy.
Organizational Impact: When multiple employees within an organization are struggling with mental health issues, it can impact the overall work environment, team dynamics, and organizational culture.
Identifying Issues: Surveys help organizations identify potential mental health issues among employees. By collecting data on stress levels, work-related challenges, and overall well-being, employers can pinpoint areas that need improvement.
Early Intervention: Early detection of mental health concerns allows employers to intervene before issues escalate. This can prevent minor challenges from turning into major problems that might lead to burnout, decreased productivity, or even long-term health issues.
Creating Supportive Environments: Surveys provide insights into whether employees feel supported in their mental health needs. This information enables organizations to create an environment where employees feel comfortable discussing mental health and seeking help when needed.
Tailored Programs: Survey data can guide the development of targeted mental health programs and initiatives. Employers can offer resources and support that align with the specific challenges their employees are facing.
Reducing Stigma: Openly discussing mental health through surveys can help reduce the stigma surrounding these issues. When employees know that their employers care about mental well-being, they are more likely to feel comfortable discussing their challenges.
Employee Engagement: Addressing mental health concerns can boost employee engagement. When employees feel their well-being is a priority, they are more likely to be engaged, motivated, and productive at work.
Retention and Recruitment: A positive approach to mental health can enhance employee retention and attract new talent. Organizations that prioritize mental well-being are often seen as more attractive places to work.
Data-Informed Decisions: Survey data provides valuable insights that can inform organizational decisions. From adjusting workloads to refining company policies, data-driven decisions can lead to a healthier and more productive workforce.
Legal and Ethical Considerations: Many jurisdictions have laws and regulations related to mental health in the workplace. Conducting surveys can help organizations demonstrate compliance and ethical responsibility in addressing employee well-being.
Overall Organizational Health: Employee mental health is closely tied to organizational health. A workforce that is mentally and emotionally well will contribute positively to the company’s overall success and growth.
Feedback Loop: Surveys establish a feedback loop, showing employees that their opinions and well-being matter to the organization. This can foster trust and a sense of partnership between employees and employers.
Incorporating mental health surveys into an organization’s practices can promote a culture of caring, support, and well-being. However, it’s essential to ensure that the collected data is treated confidentially and that actions are taken based on the survey results to genuinely make a positive impact on employee mental health.
Recognizing the potential impact of mental health issues on work performance is crucial for both employers and employees. Creating a supportive workplace that addresses mental health concerns, provides access to resources, and promotes open communication can help mitigate these negative effects and contribute to a healthier and more productive work environment.
Sign up to receive our email, delivering the latest stories straight to your inbox.